Working principle of gait analyzer
Gait analyzer is a device used to measure and analyze human walking patterns.
Its working principle is mainly based on the following technologies:
- Pressure sensing technology
Use pressure sensors (such as piezoelectric sensors, capacitive sensors) to record the pressure distribution of the sole of the foot and analyze the force point and foot load changes during gait.
Typical equipment includes plantar pressure plates or insole pressure sensors, which can measure the force conditions of various parts of the sole of the foot.
- Motion capture technology
Use optical motion capture systems (such as infrared cameras, 3D laser scanning) or inertial sensors (IMU, inertial measurement unit) to record dynamic information of human walking.
The main parameters include step length, step frequency, step speed, swing time, support time, etc.
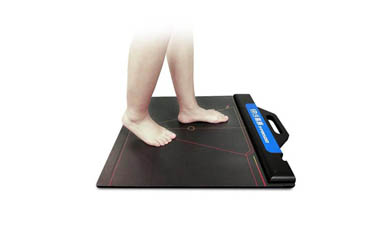
- Video analysis
Record gait with a high-speed camera, combine computer vision technology (such as AI motion analysis algorithm) to automatically detect gait abnormalities and evaluate gait patterns.
Plantar pressure distribution system
Use of gait analyzer in hospital
Gait analyzer is widely used in hospital, mainly involving the following fields:
- Orthopedics and rehabilitation medicine
Evaluate gait recovery after fracture, arthritis, scoliosis, hip or knee replacement.
Guide rehabilitation training programs, such as orthopedic insoles and gait correction training.
- Neurological disease evaluation
Used for gait analysis of patients with Parkinson’s disease, stroke, cerebral palsy, spinal cord injury, etc., to evaluate the impact of the nervous system on walking.
Monitor the degeneration of motor function and assist doctors in formulating rehabilitation strategies.
- Diabetic foot screening
Through plantar pressure analysis, the risk of diabetic foot ulcers can be detected early to prevent foot lesions.
- Sports medicine and sports injury rehabilitation
Evaluate the gait of athletes, optimize running and walking postures, and reduce the risk of sports injuries.
Monitor gait changes after sports injuries and adjust rehabilitation training plans.
- Fall risk assessment for the elderly
By detecting gait stability, step length, step frequency, etc., the risk of falls for the elderly can be predicted to help prevent falls and fractures. 6. Child development assessment
Assess children’s walking ability, detect gait abnormalities such as flat feet, inversion and valgus, X/O legs, and intervene early.
Gait analyzers can provide accurate data support in clinical applications, helping doctors to diagnose and treat diseases related to gait abnormalities more scientifically.
