The plantar pressure distribution system enables the production of corrective insoles through three core links: data collection, analysis, and design optimization. The specific application process is as follows:
1. Data collection stage
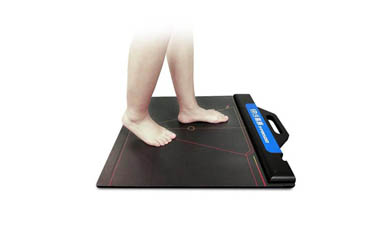
Static and dynamic pressure detection
Measure the pressure distribution of each area of the sole when standing (static) through the sensor matrix or pressure sensing pad, and identify structural abnormalities such as flat feet and high arches;
Monitor the changes in plantar pressure during walking, running and other actions (dynamic), and analyze the force characteristics of heel landing, midfoot support and forefoot push-off stages.
Combined with 3D scanning technology to obtain the geometric structure of the sole, supplement the morphological information of pressure data, and provide accurate fit support for the insole.
2. Data analysis and program formulation
Abnormal pressure point identification
The system generates a heat map to display high-pressure areas (such as the inside of the sole or the forefoot), and locates the areas that need to relieve pressure.
Gait and support mode evaluation
Combined with gait cycle data, determine foot rollover (such as inversion/externalization) and stability problems, and determine the need for correction.
Personalized design parameter output
According to the pressure distribution and arch shape, calculate the insole support height, material density, thickness distribution and other parameters .
3. Insole production and optimization
Digital molding technology
Use an engraving machine or 3D printing equipment to complete the preliminary engraving of the insole substrate according to the data model ;
Adjust the edge curvature and contact surface smoothness through manual polishing to improve comfort .
Functional verification and iteration
After the patient tries it on, the correction effect is tested again through the pressure distribution system to optimize the pressure dispersion efficiency .
4. Application effect
Correct foot abnormalities : Disperse the high-pressure area of the sole to relieve the pain of patients with flat feet, diabetic feet, etc. ;
Optimize biomechanics : Improve walking posture and joint force balance by supporting the arch and adjusting the force line of the lower limbs ;
Dynamic adaptability : Smart insoles can monitor pressure changes in real time and provide data support for long-term health management .

Pingback: Foot Scanner_Foot Shape Scanner_Gait Analysis Equipment_Gait Analyzer Manufacturer_Gait Analysis System
Pingback: Foot Scanner_Foot Shape Scanner_Gait Analysis Equipment_Gait Analyzer Manufacturer_Gait Analysis System