A foot scanner is a device used to acquire three-dimensional morphological data of the foot. It is mainly applied in the fields of custom insole manufacturing, orthotic design, foot medical diagnostics, footwear design and production. By scanning the surface of the foot, it accurately measures key dimensions such as foot length, foot width, arch height, and toe spacing, helping to achieve personalized design and precise matching.
I. Functions of the Foot Scanner
Acquire 3D data of the foot and build a foot model
Assist in foot health assessment, such as identifying structural issues like flat feet and high arches
Provide design parameters for footwear production and enable customized manufacturing
Used in the medical field to create orthotic insoles and assist in rehabilitation treatment
Improve footwear fit and comfort, reducing fatigue from wearing
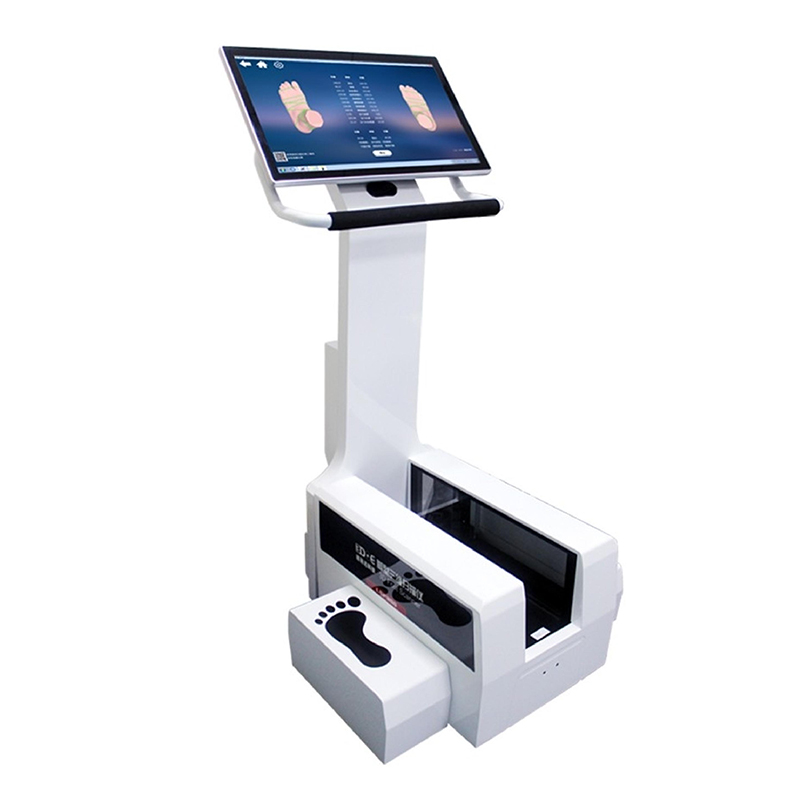
II. Working Principle of the Foot Scanner (Laser Scanning)
Foot scanners commonly use laser triangulation as their core imaging principle. This method captures the 3D shape of the foot in a non-contact manner and features high accuracy, fast speed, and strong stability.
Laser Projection
A laser in the system projects one or more laser lines (or dot patterns) onto the surface of the foot. These laser lines bend and shift according to the contours of the foot.
Imaging Collection
A high-resolution camera (or multiple cameras), fixed at a certain angle relative to the laser, synchronously records the deformation of these laser lines on the foot surface. Since there is a fixed baseline distance between the camera and the laser, spatial positioning can be calculated using geometric relationships.
Triangulation
Using the laser’s incident angle, the pixel position of the reflected light in the image, and the angle between the camera and laser, the system precisely calculates the spatial coordinates of each point on the foot surface through triangulation algorithms.
Data Reconstruction
The system stitches and fits the large number of acquired spatial points (point cloud) to generate a complete 3D model of the foot. The final output can be digital models in formats such as STL, OBJ, or PLY for use in design software.
III. Advantages of Laser Scanning
Non-contact measurement, does not affect the natural shape of the foot
High accuracy, typically up to 0.5 millimeters
Fast scanning speed, usually completes the entire foot scan in 3 to 20 seconds
Seamless integration with CAD/CAE systems for easy modeling and manufacturing
Suitable for scanning under different postures (standing, sitting, suspended) and for various populations
